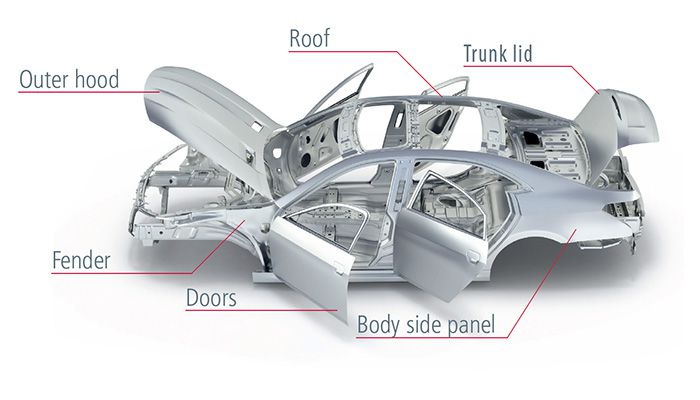
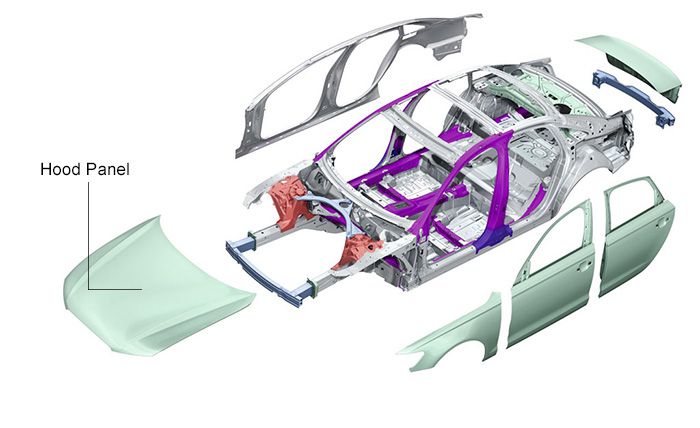
What Are Car Hoods Made of
When most people think of a car hood, they immediately think of it as "the cover that protects the engine," but they rarely consider its material selection. In fact, the hood material not only affects a car's appearance and safety, but is also closely related to fuel consumption and range.

Three Common Materials
1. Traditional Cold-Rolled Steel
Cold-rolled steel was one of the earliest materials used for hoods. Its advantages are clear: low cost, mature processing, and stable impact resistance. However, its disadvantage is also significant: heavy weight.
2. Aluminum Alloy Sheet
Aluminum sheet has been the mainstream hood material for the past decade. From B-segment cars (such as the Honda Accord and BMW 3 Series) to luxury cars (such as the Mercedes-Benz E-Class and Tesla Model 3), aluminum sheet hoods are almost universally used. It perfectly solves the pain point of steel's "heavy weight" while offering significant advantages in corrosion resistance and formability, which will be discussed in detail later.
3. Composite Materials
Some supercars and new energy concept cars are experimenting with carbon fiber composites and fiberglass reinforced plastics (FRP). These materials are 30% lighter than aluminum and offer exceptional strength. However, the downsides are high cost and difficulty in repair.
Four Core Advantages of Aluminum Sheets
1. Lightweight
Aluminum sheet has a density of approximately 2.7g/cm³, only one-third that of steel (7.8g/cm³). An aluminum hood of the same size weighs approximately 8-12kg, 5-8kg lighter than a steel one. Don't underestimate these few kilograms; they have significant impact on the overall vehicle:
For gasoline vehicles: Every 100kg weight reduction reduces fuel consumption by 0.5-0.8L per 100km. Based on an annual mileage of 10,000km, this translates to a fuel saving of 50-80L per year.
For new energy vehicles: Every 100kg weight reduction increases range by 30-50km, equivalent to a 10% increase in range, alleviating range anxiety.
2. Corrosion Resistance
Hoods are exposed to the elements for extended periods, subjecting them to the impact of rain, snow, and road debris. Aluminum sheets have a natural "protective layer"—a dense oxide film (Al₂O₃) forms on the surface, preventing further corrosion of the metal underneath. Even with long-term use, they are less susceptible to rust and bulging than steel sheets. This is why the hoods of older aluminum-clad vehicles still appear smoother than those of steel-clad models even after several years.
3. Good Formability
Modern vehicles are increasingly pursuing streamlined designs, and hoods often require complex shapes such as curved transitions and raised ridges. Aluminum sheets have greater ductility than steel sheets (elongation can reach 20%-30%), allowing them to better conform to the mold during stamping and create more refined lines.
4. High Recyclability
Automakers are now emphasizing "sustainable development." Aluminum sheet has a recycling rate of over 95%, and the recycling process consumes only 5% of the energy used by virgin aluminum. In contrast, steel plate loses strength after recycling, with a utilization rate of approximately 70%. From an environmental perspective, aluminum plate clearly aligns better with future trends.
How to Choose an Aluminum Plate Alloy
1. 5-Series Aluminum Alloy (Aluminum-Magnesium Alloy)
5-Series alloys use magnesium as the primary alloying element (3%-5%) and cannot be heat-strengthened. Their core strengths are ductility and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for stamping complex curved surfaces. Common grades for engine hoods include 5052, 5083, and 5182. You can inquire 5182 aluminum price from us directly.
A common advantage of these alloys is their ease of welding repair. Minor collisions can be repaired using sheet metal, resulting in repair costs approximately 30% lower than those of the 6-Series. For example, 5182 alloy boasts an elongation of over 18%, making it easy to achieve the seamless, streamlined curves of the Tesla Model 3.
2. 6-Series Aluminum Alloys (Aluminum-Magnesium-Silicon Alloys)
6-Series alloys contain magnesium and silicon (a total of 2%-4%) and can be strengthened through heat treatment, resulting in significantly higher strength than 5-Series alloys. Common grades include 6016, 6061, and 6111.
6016 alloy is a star grade among these alloys, developed by Alcoa specifically for automotive body panels. Its fatigue strength surpasses that of ordinary steel. The BMW 7 Series's use of this grade reduced the weight of its hood by 15kg and improved fuel efficiency by 8%. 6061 aluminum, due to its high strength, is the preferred choice for SUVs.
Original Source:https://www.autoaluminumsheet.com/a/what-are-car-hoods-made-of.html
Tags: 5182 aluminum sheet ,
Prev:The Requirements of Automotive Aluminum Sheet on Timeliness
Next:What Are 6061 Car Aluminum Properties